Penile Implant for Patients with Prostate Cancer
 The radical prostatectomy is performed upon patients with prostate cancer in the hope of curing this disease. Unfortunately, this procedure can result in erectile dysfunction (ED). The 3 piece penile implant is by far the most successful treatment for ED in this setting.
The radical prostatectomy is performed upon patients with prostate cancer in the hope of curing this disease. Unfortunately, this procedure can result in erectile dysfunction (ED). The 3 piece penile implant is by far the most successful treatment for ED in this setting.
The Radical Prostatectomy for Prostate Cancer
If you have prostate cancer that is confined to the prostate and if you have at least a 10-year life expectancy – the best treatment for your cancer is radical prostatectomy. This surgery removes the entire prostate gland.
The two most important complications of this surgery are urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction (ED). This surgery can cause ED due to injury of the cavernosal nerves. The cavernosal nerves innervate the penis and they are critically important to the erection process. The nerves are located adjacent to the posterior surface of the prostate. Consequently, when the prostate is excised, the nerves can be injured.
The Nerve Sparing Radical Prostatectomy
If you have prostate cancer, you may have a favorable form of the disease. Your doctor, such as brooklyn urologist Dr. Jon Lazare, can determine if you have a favorable disease based upon a physical exam of your prostate and based upon the results of your prostate biopsy. Finally, your doctor can obtain an MRI of your prostate gland and the results will further help determine if your cancer is favorable.
If your doctor determines that you have favorable prostate cancer, you may undergo a nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy. This procedure avoids injury to the cavernosal nerves which are vitally important to the erection. The nerve-sparing procedure can only be performed in the setting of favorable prostate cancer. Almost two-thirds of patients who undergo the nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy will retain potency after their procedure[1].
Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy – RALP
 Currently, more than 70% of patients who undergo radical prostatectomy – now undergo the Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy or RALP procedure[2]. This modern version of the radical prostatectomy is much less invasive because it avoids a skin incision. The RALP procedure is called “minimally invasive” and it uses advanced fiber-optic telescopes and specially designed instruments. The scopes and instruments are inserted into the abdomen through ports. Ports are small circular openings in the wall of the abdomen.
Currently, more than 70% of patients who undergo radical prostatectomy – now undergo the Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy or RALP procedure[2]. This modern version of the radical prostatectomy is much less invasive because it avoids a skin incision. The RALP procedure is called “minimally invasive” and it uses advanced fiber-optic telescopes and specially designed instruments. The scopes and instruments are inserted into the abdomen through ports. Ports are small circular openings in the wall of the abdomen.
Despite these impressive advances in technology, the RALP still causes erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence in a significant number of patients.
How Does the Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy Cause Sexual Dysfunction?
Sexual dysfunction following the RALP tends to be severe and difficult to treat. The RALP procedure can cause sexual dysfunction for the following several reasons:
- The RALP can damage the cavernosal nerves that are vital to the erection.
- The RALP can damage the blood supply to the penis.
- The RALP can cause scarring of the corpora cavernosa. The corpora are two long cylinders that run the length of the penis and they play a critical role in the erection.
- Scarring of the corpora cavernosa can also reduce the length of the penis
- The RALP completely removes the prostate. This results in a dry ejaculate – no fluid comes out during orgasm.
- The RALP can produce urinary incontinence. Leakage of urine can decrease libido and interfere with overall sexual function.
- The RALP procedure can produce climacteric – the passage of urine during orgasm.
Treatment of ED – Conservative Therapy
Conservative therapies for the treatment of ED include Viagra, self–injection therapy with prostaglandin E1, and the penile vacuum erection device. Unfortunately, these conservative measures do not work well in this group of patients[3].
Penile Implant – Surgical Considerations
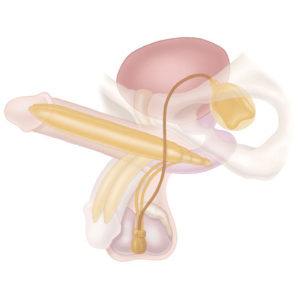 The RALP presents a unique clinical situation for your surgeon who will insert your 3-piece penile implant. Your surgeon must consider the following when he inserts the penile implant:
The RALP presents a unique clinical situation for your surgeon who will insert your 3-piece penile implant. Your surgeon must consider the following when he inserts the penile implant:
First, the RALP procedure can cause damage and scarring to the corpora cavernosa of the penis. The corpora cavernosa are two cylinders that run the full length of the penis and they are responsible for the erection.
The penile implant procedure involves dilation of the corpora cavernosa prior to placement of the implant. Because the corpora are often scarred after the RALP, your surgeon has to take extra care not to perforate the corpora during the dilation step. Perforation of the corpora can lead to damage of the urethra and incorrect positioning of the implant device.
Second, the RALP procedure may cause scarring in the space surrounding the urinary bladder. Many implant surgeons place the implant reservoir in this space. Scarring of this space can make reservoir placement more difficult and more dangerous. Scarring of this space surrounding the bladder increases the risk of bladder injury, vascular injury, and bowel injury during reservoir placement.
Therefore, in patients who have undergone the RALP, it is better to place the reservoir in an alternate location – in the abdominal wall beneath the rectus muscle. Placing the reservoir in this alternate location completely eliminates the risks associated with placing the reservoir near the urinary bladder[4].
The AMS Conceal Reservoir
The American Medical Systems (AMS) Conceal reservoir was specifically designed for patients who undergo the RALP procedure for prostate cancer. The Conceal reservoir is flat as a pancake. When it is placed in the abdominal wall, it is barely noticeable. Satisfaction rates with this new reservoir placed in the abdominal wall are identical to satisfaction rates with reservoir placement next to the urinary bladder. And again, the placement of the reservoir in the abdominal wall is completely safe.
Complications of the Penile Implant
 The main complications of the penile implant include device infection, device erosion, and mechanical failure. The complication rate among patients who have undergone the RALP procedure is the same as the overall complication rate for all patients who undergo penile implant insertion[5].
The main complications of the penile implant include device infection, device erosion, and mechanical failure. The complication rate among patients who have undergone the RALP procedure is the same as the overall complication rate for all patients who undergo penile implant insertion[5].
Success Rate of Penile Implant
The success rate of penile implantation in this group of patients is high. Treatment satisfaction rates exceed 90% and satisfactory sexual function rates exceed 80%. These results are impressive considering the severity of sexual dysfunction among these patients with prostate cancer.
Early Penile Implant Placement
Patients who undergo the penile implant during or shortly after the RALP procedure have better overall results than those patients who receive the implant one or two years later. Not only are success rates higher, but the loss of penile length can be completely avoided with early implant placement[6].
Early implant placement should be considered in patients who have ED prior to the RALP procedure or in those patients who are not candidates for the nerve-sparing procedure. All other patients should wait at least two years after the RALP before penile implant insertion.
Simultaneous Insertion of the Penile Implant and the Artificial Urinary Sphincter
 Patients who undergo the RALP procedure may suffer from ED and urinary incontinence. Placement of both the 3 penile implant and the artificial urinary sphincter can be performed at the same time in patients who suffer from ED and urinary incontinence. The success rate of the simultaneous procedure is high. The main disadvantage is that the risk of penile implant infection increases in the presence of the artificial urinary sphincter[7].
Patients who undergo the RALP procedure may suffer from ED and urinary incontinence. Placement of both the 3 penile implant and the artificial urinary sphincter can be performed at the same time in patients who suffer from ED and urinary incontinence. The success rate of the simultaneous procedure is high. The main disadvantage is that the risk of penile implant infection increases in the presence of the artificial urinary sphincter[7].
CALL NOW: (718) 795-2594
References
[1] Tal, R, Alphs, H, Krebs, P, Nelson, C, Mulhall, J, Erectile Function Recovery Rates After Radical Prostatectomy. A meta-analysis. Journal of Sexual Medicine, 2009, 6:2538-2546
[2] Lowrance, W, Eastham, J, Savage, C, Contemporary Open and Radical Prostatectomy Practice Patterns Among Urologists in the United States, Journal of Urology, 2012, 187:2087
[3] Mulhall, J, Slovick, R, Hotaling, J, Erectile Function After Radical Prostatectomy: Hemodynamic Profiles and Their Correlation With The Recovery of Erectile Function, Journal of Urology, 2002, 167, 3. 1371-1375
[4] Karpman, E, Brant, W, Kansas, B, Bella, A, Jones, L, Eisenhart, E, Henry, G, Reservoir Alternate Surgical Implantation Technique: Preliminary Outcomes Of Initial PROPPER Study of Low Profile Spherical Resevoir Implantation in Submucosal Location or Traditional Prevesical Space, The Journal of Urology, Vol. 193, 239-244, January 2015
[5] Menard, J, Tremeaux, j, Faix, A, Pierrevelcin, J, Staerman, F, Erectile Function and Sexual Satisfaction Before and After Penile Prosthesis Implantation In Radical Prostatectomy Patients: A Comparison With Patients With Vasculogenic Erectile Dysfunction, Journal of Sexual Medicine, 2011, 8, 3479-3486
[6] Mondaini, N, Cai, T, Sarti, E, Polloni, G, Gavazzi, A, Conti, D, Cocci, A, Albersen, M, Cito, G, Bartoletti, R, A Case Series of Patients Who Underwent Laparoscopic Extraperitoneal Radical Prostatectomy With the Simultaneous Implant of a Penile Prosthesis: Focus On Penile Length Preservation, World Journal of Men’s Health, 2018, May, 36, 2, 132-138
[7] Patel, N, Golan, R, Halpern, J, Sun, T, Asafu-Adjei, A, Chughtai, B, Stahl, P, Sedrakyan, A, Kashanian, J, A Contemporary Analysis of Dual Inflatable Penile Prosthesis and Artificial Urinary Sphincter Outcomes, The Journal of Urology, Vol. 201, 141-146, January 2019
